二叉树遍历。
深度优先遍历和广度优先遍历
二叉树的遍历可以使用深度优先遍历(DFS,Depth-First-Search)和广度优先遍历(BFS,Breadth-First-Search),可以使用递归算法和非递归算法实现。
递归算法性能并无优势,但是可读性好,非递归算法的性能更优。
深度优先遍历按照遍历的次序可以分为三种:
- 前序遍历(dlr):根-左-右
- 中序遍历(ldr):左-根-右
- 后序遍历(lrd):左-右-根
首先构造出一个二叉树:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| const nodes = {
node: 100,
left: {
node: 5,
left: {
node: 4,
left: {
node: 6,
},
right: {
node: 7,
left: {
node: 200,
},
right: {
node: 300
}
}
},
right: {
node: 3,
right: {
node: 8
}
}
},
right: {
node: 2,
right: {
node: 1
}
}
};
|
结果:
深度优先遍历 - 前序遍历
先访问根节点,然后访问左节点、右节点:
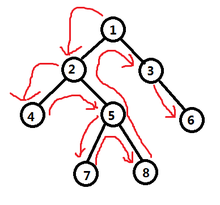
(1)使用递归算法:
- 如果二叉树为空,则遍历结束,否则
- 访问根节点
- 前序遍历根节点的左子树
- 前序遍历根节点的右子树
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
function dfs_dlr_1(nodes, result = []) {
if (nodes.node) {
result.push(nodes.node);
nodes.left && dfs_dlr_1(nodes.left, result);
nodes.right && dfs_dlr_1(nodes.right, result);
}
return result
}
|
(2)使用非递归算法:
需要借助一个栈(后入先出),通过不断的压入和取出来实现,关键点是①使用栈而非队列②先push右子树再push左子树
- 初始化一个栈,将根节点压入栈中
- 档栈非空时,循环执行步骤3、4,否则结束
- 取出栈顶节点,节点值放入结果数组
- 如果该节点的右子树非空,则将右子树压入栈,如果该节点的左子树非空,则将左子树压入栈
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
function dfs_dlr_2(nodes) {
let result = [];
let stack = [];
stack.push(nodes);
while (stack.length > 0) {
const target = stack.pop();
result.push(target.node);
target.right && stack.push(target.right);
target.left && stack.push(target.left);
}
return result;
}
|
深度优先遍历 - 中序遍历
先访问左子树,然后访问根节点,最后访问右子树
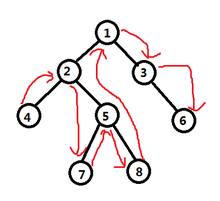
(1)使用递归算法:
- 如果二叉树为空,则遍历结束,否则
- 中序遍历访问根节点的左子树
- 访问根节点
- 中序遍历访问根节点的右子树
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
function dfs_ldr_1(nodes, result = []) {
if (nodes.node) {
nodes.left && dfs_ldr_1(nodes.left, result);
result.push(nodes.node);
nodes.right && dfs_ldr_1(nodes.right, result);
}
return result;
}
|
(2)使用非递归算法:
- 借助一个栈,当栈为空时结束遍历
- 进入遍历,判断当前节点的左子树是否存在,如果存在则将当前节点压入栈中,然后将当前节点替换为其左子树
- 当前节点不再存在左子树时,意味着找到了整棵树最左下角的节点,出栈一项,记录当前节点的值
- 将当前节点替换为出栈项的右子树,重复2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
function dfs_ldr_2(nodes) {
let result = [],
stack = [],
root = nodes;
while (true) {
while (root) {
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
if (stack.length === 0) {
break;
}
const current = stack.pop();
result.push(current.node);
root = current.right;
}
return result;
}
|
深度优先遍历 - 后序遍历
先访问子树,然后访问根节点。
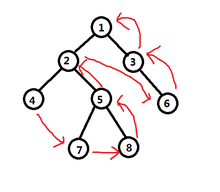
(1)递归算法:
- 如果二叉树为空,则遍历结束,否则
- 访问根节点
- 前序遍历根节点的左子树
- 前序遍历根节点的右子树
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
function dfs_lrd_1(nodes, result = []) {
if (nodes.node) {
nodes.left && dfs_lrd_1(nodes.left, result);
nodes.right && dfs_lrd_1(nodes.right, result);
result.push(nodes.node);
}
return result
}
|
(2)使用非递归算法:
- 可以调整前序遍历的算法,前序遍历计算的是『根-左-右』
- 可以调整压入栈的顺序,将前序遍历中的先压入右子树调整为限压入左子树,调整后的顺序是『根-右-左』
- 后续遍历的顺序是
『左-右-根』 = 『根-右-左』.reverse();
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
function dfs_lrd_2(nodes) {
let result = [],
stack = [nodes];
while (stack.length > 0) {
const current = stack.pop();
result.push(current.node);
current.left && stack.push(current.left);
current.right && stack.push(current.right);
}
return result.reverse();
}
|
广度优先搜索
一层一层从左至右向下遍历
(没有用递归实现)
- 通过一个队列实现(先入先出),将后续的左节点、右节点分别加入队列
- 一层一层向下进行
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
function bfs_1(nodes) {
let result = [];
let queue = [nodes];
while (queue.length > 0) {
const current = queue.shift();
result.push(current.node);
current.left && queue.push(current.left);
current.right && queue.push(current.right);
}
return result;
}
|
二叉树最大深度
思路:使用使用广度优先搜索实现,队列中构造了一个标志level,用来标识当前深度(应该有更好的方式)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
function getDepth(nodes) {
let currentDepth = 0;
let queue = [{value: nodes, depth: 1}];
while (queue.length > 0) {
const current = queue.shift();
const currentNode = current.value;
currentDepth = Math.max(currentDepth, current.depth);
currentNode.left && queue.push({value: currentNode.left, depth: currentDepth + 1});
currentNode.right && queue.push({value: currentNode.right, depth: currentDepth + 1});
}
return currentDepth;
}
|
二叉树翻转
思路:如果根节点不为空,则将左右子节点交换,然后将左右子节点进行递归调用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| const reverseTree = tree => {
if (tree) {
[tree.left, tree.right] = [tree.right, tree.left];
reverseTree(tree.left);
reverseTree(tree.right)
}
return tree
}
|
参考



